“Hey Craig - we’re going to Belize to make a movie about the Crystal Skull of the Maya. Want to come?” My cousin Anthony Conforti was a film maker and I couldn’t refuse. It was 1987. We filmed the Maya doing the Deer Dance and a local farmer took me to see a cocoa grove. I was blown away, I had never seen cocoa trees, with yellow and red pods growing out of the stems of the trees. That evening I wrote in my diary a plan for a chocolate spread called Whole Earth ‘Maya Maya’ – a Nutella-like concoction of peanuts, cohune oil and date juice. It didn’t happen, but the dream wouldn’t go away.
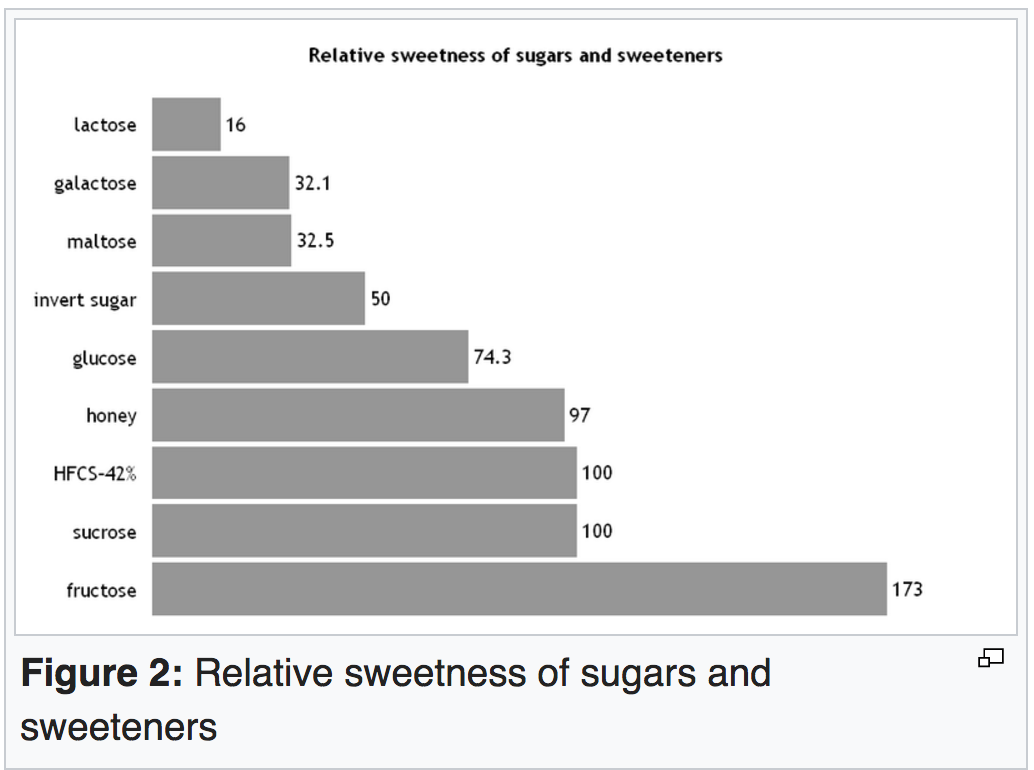
A few years later André Deberdt, a French organic consultant in Togo offered me organic peanuts. They were delicious but failed our aflatoxin test. I called him up with the bad news. “They grow organic cacao, too’ he commented. I had read that 70% chocolate had a tiny glycemic index: 21 compared to 60 of brown rice, so we got a sample made. It was mind blowing. My girl friend Jo Fairley fell in love with it and came up with the name ‘Green’ for organic and ‘Black’ for being the darkest chocolate on the market. We launched 30 years ago, in 1991. It was the first chocolate that talked openly about its provenance – farmers in Togo who were regenerating their farmland by going organic. It was a hit.
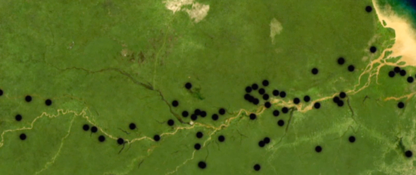
In 1993 I got in touch with some friends in Belize and found that the cacao farmers were in big trouble: they had borrowed money to plant cacao trees on assurances from the US Peace Corps and Hershey that they would be getting $1.75 lb a few years later. By the time they were cropping, the price was $0.55. Farmers abandoned the cacao but now had bank debt. Sainsbury’s said they’d stock our idea of ‘Maya Gold’ if we would give them a 6 month exclusive. So I offered the Maya farmers $1.25 and a 5 year rolling contract and put $20,000 prepayment in their bank to keep their bank manager on side. The Fairtrade Foundation suggested it could be a product to launch their Mark and flew out to Belize to validate what we were doing and said ‘It’s all we are looking for…and more.’
So in March 1994 the Fairtrade Mark was launched to the world on Green & Black’s Maya Gold chocolate. All the supporters of Fairtrade now had something to sink their teeth into, both literally and campaigning-wise. Tesco, Safeway and Waitrose were all asking for it and Sainsbury’s nobly let us off the exclusive deal in the shared interest of seeing Fairtrade take off. Within a year the Fairtrade Mark was on coffee, tea, bananas, and sugar and became a must stock category for natural food stores and supermarkets.
Green & Black’s grew and grew. We made milk chocolate and cocoa and hot chocolate, working with the finest artisan chocolate makers in the world. (I’ve never made a bar of chocolate myself)
In 1999 we sold some shares to a group of people led by William Kendall, who wanted to invest. With a humungous marketing budget we grew the brand in a way that had never been possible before.
By 2005 we had gone from £1.5 million turnover to £26 million turnover. Cadbury’s bought the business. Then they got gobbled up by Kraft. In November 2012 Tim Cofer, the CEO of Kraft, called me up to say that tomorrow he was announcing in Abidjan a $400 million plan called Cocoa Life that would build on what we had done in Belize with Fairtrade. They appointed women to run the programme in Ghana and Ivory Coast and it has been hugely successful, with farmers queuing up to be part of it. Now it is going to the Dominican Republic, where most of the organic cacao is grown. Green & Black’s has just enjoyed a massive advertising push, with a stunning video that simply says “Wildly, Deliciously, Organic.” The entire organic market benefits when a brand like Green & Black’s or Yeo Valley establishes the organic version in a product category as a leader.
Jo and I still work with the team at Green & Black’s, having a moan when we think they are going off piste and patting them on the backs when they get it right. We’ve had nothing to moan about for quite a while, in fact we are very proud of how well our erstwhile baby is growing